Ukraine news dominates global headlines, detailing a multifaceted conflict impacting not only Ukraine but also the global political, economic, and humanitarian landscape. This ongoing war has spurred a significant humanitarian crisis, displacing millions and straining international aid efforts. Beyond the immediate battlefield, the conflict’s economic repercussions are far-reaching, impacting global energy markets and food security. Understanding the complexities of this situation requires examining the military strategies, political maneuvering, international responses, and the long-term consequences for Ukraine and the world.
From the ongoing military conflict and its devastating humanitarian consequences to the significant geopolitical shifts and far-reaching economic impacts, the situation in Ukraine demands a comprehensive understanding. This analysis explores the current military stalemate, the evolving political alliances, the international community’s response, and the profound social and cultural ramifications of the conflict. We will also delve into the challenges of rebuilding Ukraine, addressing war crimes, and considering the long-term implications for regional stability.
Current Military Situation
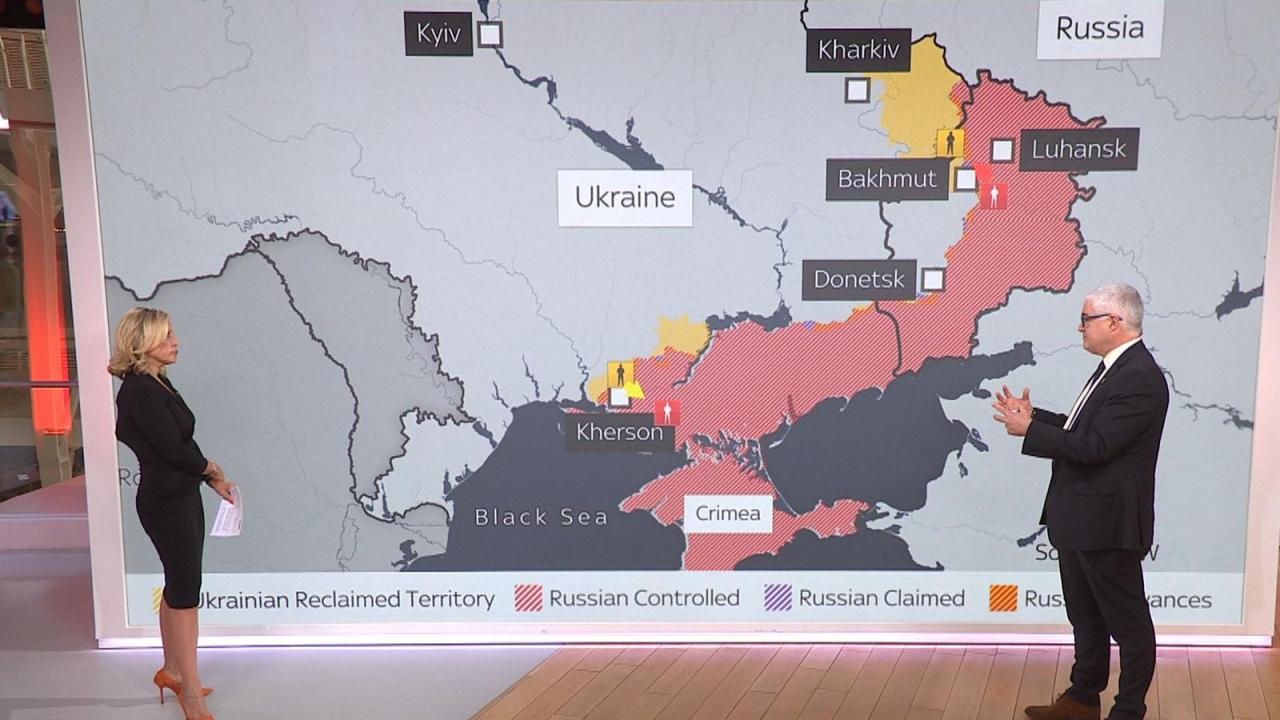
The conflict in Ukraine continues to be a dynamic and complex situation, with the frontline shifting gradually over time. Understanding the current military disposition, the contrasting strategies employed by both sides, and the influence of Western aid is crucial to analyzing the ongoing conflict.
Frontline Positions
The eastern and southern fronts remain the most active areas of conflict. In the east, fighting is concentrated around the Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts, with intense battles for control of key towns and villages. The southern front sees ongoing fighting along the Kherson and Zaporizhzhia regions, with both sides vying for territorial gains and strategic advantages. The precise location of the frontline is fluid and subject to daily changes, making precise mapping challenging. Reports from various sources, including military analysts and independent observers, provide a general understanding of the overall situation, though precise details often remain unclear due to the ongoing nature of the conflict and the inherent difficulties in verifying information from the battlefield.
Military Strategies: Russia vs. Ukraine
Russia’s military strategy has largely focused on a grinding war of attrition, employing overwhelming artillery barrages and leveraging its numerical superiority in manpower and equipment. This approach has been criticized for its high casualty rate and slow progress. In contrast, Ukraine has adopted a more flexible strategy, focusing on precision strikes, utilizing Western-supplied weaponry, and leveraging effective defensive tactics. Ukraine’s strategy aims to maximize the impact of its limited resources, focusing on strategically important targets and exploiting Russian weaknesses. The effectiveness of each strategy is a subject of ongoing debate among military experts, with the ultimate outcome dependent on a multitude of factors including the continued flow of Western aid and the overall endurance of both combatants.
Impact of Western Military Aid
Western military aid has been instrumental in shaping the course of the conflict. The provision of advanced weaponry, including HIMARS rocket systems and various anti-tank and anti-aircraft systems, has significantly enhanced Ukraine’s defensive capabilities and offensive potential. This aid has allowed Ukraine to target Russian logistics and command centers, disrupting Russian operations and limiting their effectiveness. The continued supply of ammunition, training, and intelligence sharing are also critical components of this support, ensuring Ukraine’s ability to sustain its resistance. However, the extent to which Western aid can ultimately determine the outcome of the war remains to be seen, as the conflict’s duration and intensity continue to evolve.
Hypothetical Ceasefire Agreement
A potential ceasefire agreement might involve a phased withdrawal of Russian forces from occupied Ukrainian territories, a commitment to uphold Ukraine’s territorial integrity within its internationally recognized borders, and the establishment of a robust international peacekeeping force to monitor the implementation of the agreement. Such an agreement would also likely involve provisions for addressing the humanitarian crisis, facilitating the return of refugees, and establishing mechanisms for resolving long-term security concerns. This scenario, however, is highly complex and depends on the willingness of both sides to engage in meaningful negotiations, which currently appears unlikely given the ongoing hostilities and deep-seated mistrust between the parties involved. Similar attempts at negotiated settlements in other conflicts, such as the Korean War armistice, could serve as models for the potential structure and challenges of such an agreement. However, each conflict presents its own unique complexities, requiring tailored approaches.
Humanitarian Crisis
The ongoing war in Ukraine has triggered a profound humanitarian crisis, impacting millions of civilians. The scale of destruction and displacement necessitates a massive and sustained international relief effort. The needs are vast and constantly evolving, requiring a flexible and adaptable response from aid organizations.
Current Humanitarian Needs in Ukraine
The humanitarian needs in Ukraine are multifaceted and extensive. These include access to food, water, shelter, medical care, and psychosocial support. Millions are facing food insecurity, with limited access to essential supplies due to damaged infrastructure and ongoing conflict. The destruction of healthcare facilities has severely hampered access to medical services, leaving many vulnerable to preventable diseases and injuries. The constant shelling and displacement have also created a significant mental health crisis, impacting both adults and children. Furthermore, the destruction of homes and infrastructure has left millions without adequate shelter, especially in winter conditions.
Internally Displaced Persons and Refugees
The conflict has resulted in a massive displacement of people both within Ukraine and across its borders. The UNHCR estimates millions have been internally displaced, seeking refuge in safer regions within the country, often facing overcrowded and inadequate living conditions. Millions more have fled to neighboring countries, seeking safety and assistance. These figures are dynamic and fluctuate depending on the intensity of fighting and the availability of safe passage. For example, initial estimates of refugees may have underestimated the true numbers as the conflict evolved. The long-term impact of this displacement will require significant and sustained support for both the displaced and the host communities.
Challenges Faced by Aid Organizations
Aid organizations operating in Ukraine face numerous significant challenges. These include navigating active conflict zones, ensuring the safety and security of their personnel, accessing affected populations, and overcoming logistical hurdles in delivering aid. The destruction of infrastructure, including roads and bridges, severely hinders the transportation of essential supplies. Bureaucratic obstacles and security concerns can also delay or prevent aid delivery. Furthermore, funding limitations often restrict the scope and reach of humanitarian interventions. The constant threat of attacks on civilian infrastructure and aid convoys adds another layer of complexity and risk.
International Organizations Involved in Humanitarian Relief Efforts
Numerous international organizations are actively involved in providing humanitarian assistance in Ukraine. These include the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), the World Food Programme (WFP), UNICEF, and Doctors Without Borders (Médecins Sans Frontières). These organizations coordinate their efforts to address the diverse needs of the affected population, working closely with local partners and governments to ensure efficient and effective aid delivery. Each organization brings specific expertise and resources to the table, collectively aiming to alleviate suffering and promote recovery. The collaborative nature of this response is crucial given the scale and complexity of the humanitarian crisis.
Political Developments: Ukraine News
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has profoundly reshaped the geopolitical landscape, triggering significant political developments both within the country and internationally. The war’s impact extends far beyond military actions, significantly altering alliances and exposing fault lines in the global order. Understanding these political shifts is crucial to comprehending the conflict’s trajectory and long-term consequences.
The key political figures involved represent a complex web of national and international actors.
Key Political Figures
Volodymyr Zelenskyy, Ukraine’s President, has become a global symbol of resistance, galvanizing international support and shaping the narrative of the conflict. His leadership has been instrumental in securing military and humanitarian aid from numerous countries. Vladimir Putin, President of Russia, is the driving force behind the invasion, his decisions dictating the course of the war and triggering widespread international condemnation. Other significant figures include key members of both the Ukrainian and Russian governments, as well as international leaders such as President Biden (USA), President Macron (France), and Chancellor Scholz (Germany), whose decisions directly influence the level of support provided to Ukraine.
Current Political Alliances and Their Influence
The war has solidified existing alliances and forged new ones. NATO, while not directly involved in military conflict with Russia, has provided significant military aid to Ukraine and increased its presence in Eastern Europe. The European Union has imposed unprecedented sanctions on Russia, demonstrating a unified response to the aggression. Conversely, countries like China and India have maintained a more neutral stance, navigating complex economic and geopolitical considerations. These differing approaches reflect a global division on how to respond to Russia’s actions, with the alliances formed and strengthened during the conflict shaping future geopolitical dynamics.
Stances of Different World Powers
The global response to the conflict has been highly polarized. The United States and its allies in NATO have provided extensive military and financial aid to Ukraine, viewing the conflict as a crucial test of international law and democratic values. The European Union has mirrored this support, albeit with internal debates regarding the economic impact of sanctions. Conversely, countries like China have refrained from condemning Russia’s actions explicitly, prioritizing their economic relationship with Russia and expressing concerns about escalating the conflict. This divergence in approaches highlights the complex interplay of national interests and ideological positions in shaping the international response.
Political Implications on Regional Stability
The conflict has dramatically destabilized the region. The ongoing fighting has displaced millions of Ukrainians, creating a humanitarian crisis and straining the resources of neighboring countries. The potential for the conflict to escalate beyond Ukraine’s borders remains a significant concern, particularly given Russia’s military presence in neighboring countries. The long-term political implications include the potential for increased militarization in Eastern Europe, a reshaping of geopolitical alliances, and the erosion of international norms regarding state sovereignty and territorial integrity. The conflict’s impact on regional stability is likely to be felt for years to come, potentially leading to protracted instability and renewed conflicts in the region.
Economic Impact
The war in Ukraine has triggered a devastating economic crisis within the country and sent significant ripple effects across the global economy. The scale of the destruction, coupled with disruptions to supply chains and energy markets, has resulted in substantial losses and widespread uncertainty. This section details the key economic consequences of the conflict.
Impact on the Ukrainian Economy
The Ukrainian economy has suffered immensely. Pre-war estimates projected a steady, if modest, growth trajectory. However, the invasion has led to widespread destruction of infrastructure, businesses, and agricultural lands. Millions of Ukrainians have fled the country, resulting in a significant loss of the workforce and consumer spending. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects a sharp contraction in Ukraine’s GDP in 2023, though the precise figure remains highly uncertain given the ongoing conflict. Reconstruction costs are estimated to be in the hundreds of billions of dollars. The World Bank estimates that rebuilding Ukraine will require a significant and sustained international effort. The damage extends beyond physical infrastructure to include the erosion of human capital and institutional capacity.
Impact on Global Energy Markets, Ukraine news
Ukraine and Russia are major exporters of energy resources, particularly natural gas and oil. The war has significantly disrupted these markets, leading to price volatility and shortages in some regions. Sanctions imposed on Russia have further complicated the situation, forcing countries to seek alternative energy sources and driving up prices globally. The impact has been felt most acutely in Europe, which is heavily reliant on Russian natural gas. This energy crisis has fueled inflation and added to economic uncertainty worldwide. For example, the price of natural gas in Europe spiked dramatically in the months following the invasion, impacting businesses and consumers alike. This has led to increased energy poverty and concerns about the reliability of energy supplies.
Impact on Ukrainian Agriculture and Food Security
Ukraine is a major global exporter of agricultural products, including wheat, corn, and sunflower oil. The war has severely disrupted agricultural production and export capabilities. Blockades of Ukrainian ports, damage to farmland and agricultural infrastructure, and the displacement of farmers have all contributed to reduced harvests and hampered exports. This has had significant consequences for global food security, particularly in countries that rely heavily on Ukrainian grain imports. The disruption of Ukrainian agricultural exports has contributed to rising global food prices and increased food insecurity in vulnerable populations worldwide. The situation is further complicated by the destruction of grain silos and the difficulty in transporting grain to export terminals.
Comparison of Pre-War and Current Economic Indicators for Ukraine
| Indicator | Pre-War (2021 Estimate) | Current (2023 Estimate) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 3.4% | -35% (IMF projection) | IMF |
| Inflation (%) | 10% | >20% (estimated) | World Bank |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 9% | >20% (estimated) | Various sources |
| Foreign Direct Investment (USD Billion) | 4.0 | <1.0 (estimated) | UNCTAD |
International Relations
The war in Ukraine has profoundly reshaped the global geopolitical landscape, significantly impacting international relations and prompting a complex web of responses from various nations and international bodies. The conflict has tested the effectiveness of existing international mechanisms and spurred debates on the future of global security architecture.
The response to the crisis has been multifaceted, encompassing diplomatic efforts, economic sanctions, and humanitarian aid, all of which have been shaped by pre-existing alliances and national interests.
The Roles of the UN and NATO
The United Nations has played a crucial, albeit often criticized, role. The UN General Assembly has overwhelmingly condemned Russia’s aggression, passing resolutions demanding a withdrawal of troops and highlighting the humanitarian crisis. However, the UN Security Council, hampered by Russia’s veto power, has been largely ineffective in enforcing these resolutions. NATO, a military alliance, has provided significant military and financial support to Ukraine, although it has avoided direct military intervention to prevent further escalation. This approach, while aiming to deter further Russian aggression, has also drawn criticism for potentially prolonging the conflict.
Impact of Sanctions on Russia
The international community, led by the US and the EU, has imposed a wide range of sanctions on Russia, targeting its financial institutions, energy sector, and key individuals. These sanctions aim to cripple the Russian economy, limiting its ability to fund the war effort. While the impact of sanctions has been debated, there is evidence suggesting a significant negative impact on the Russian economy, including inflation, capital flight, and reduced access to international markets. However, the sanctions have also had unintended consequences, affecting global energy prices and contributing to global inflation. For example, the restrictions on Russian oil and gas exports have led to increased energy costs in many countries.
Diplomatic Efforts to Resolve the Conflict
Numerous diplomatic efforts have been undertaken to negotiate a peaceful resolution, including talks between Ukraine and Russia, as well as mediation attempts by various countries and international organizations. These efforts have yielded limited success, largely due to the deeply entrenched positions of both sides and the ongoing military conflict. The Minsk agreements, a previous attempt at peace negotiations, have proven largely ineffective. The ongoing dialogue highlights the complexity of achieving a lasting peace settlement, requiring significant concessions and a commitment to long-term stability from all involved parties.
International Responses to the Humanitarian Crisis
The humanitarian crisis resulting from the war has prompted a significant international response. Many countries and international organizations have provided substantial humanitarian aid, including food, medical supplies, and shelter, to those affected by the conflict, both within Ukraine and in neighboring countries hosting refugees. The scale and nature of this aid have varied, reflecting differing capacities and priorities of different actors. The EU and the UN have been particularly active in coordinating and delivering aid, although challenges remain in reaching those in need in conflict zones and ensuring equitable distribution of resources. The speed and scale of the refugee crisis has also highlighted the need for improved international cooperation in managing large-scale displacement.
Social Impact
The war in Ukraine has had a devastating and multifaceted impact on Ukrainian society, extending far beyond the immediate physical destruction. The conflict has fractured communities, traumatized individuals, and fundamentally altered the social fabric of the nation. The long-term consequences are still unfolding, but the immediate effects are profoundly felt across all aspects of daily life.
The pervasive sense of fear and uncertainty is perhaps the most significant social consequence. Millions have been displaced, both internally and externally, leading to family separations, loss of livelihoods, and the disruption of established social networks. This displacement has created immense strain on resources in host communities, both within Ukraine and in neighboring countries. The constant threat of violence and the pervasive experience of trauma have contributed to widespread mental health challenges, requiring significant resources and support.
Impact on Education and Healthcare Systems
The war has severely disrupted both the education and healthcare systems in Ukraine. Schools and universities have been damaged or destroyed, forcing many institutions to operate online or relocate. The disruption of education has affected millions of children and young adults, hindering their academic progress and future opportunities. Similarly, the healthcare system has been overwhelmed by the influx of wounded soldiers and civilians. Hospitals have been targeted, medical supplies are scarce in many areas, and healthcare professionals face immense pressure and risks while providing care. The long-term consequences of this disruption could include a generation of children with interrupted education and a healthcare system struggling to meet the needs of a population facing significant health challenges. For example, access to routine childhood vaccinations has been significantly impacted, potentially leading to outbreaks of preventable diseases in the future.
Resilience of the Ukrainian People
Despite the immense challenges, the resilience of the Ukrainian people is evident throughout the conflict. Stories of ordinary citizens providing aid to their neighbors, volunteering in defense efforts, and maintaining a sense of national unity amidst immense suffering are numerous. For example, countless volunteers have organized aid distribution networks, providing food, shelter, and medical supplies to those in need. Teachers continue to educate children in makeshift classrooms, even under shelling. Medical professionals continue to treat patients despite the constant threat of danger. These acts of courage and solidarity demonstrate the unwavering spirit of the Ukrainian people in the face of adversity. These are not isolated incidents, but rather a reflection of a collective determination to persevere and rebuild.
Challenges Faced by Ukrainian Civilians
The challenges faced by Ukrainian civilians are extensive and interconnected.
- Displacement and Loss of Housing: Millions have been forced to flee their homes, facing homelessness and the loss of personal belongings.
- Food Insecurity: Disrupted supply chains and the destruction of agricultural lands have led to food shortages and rising prices.
- Lack of Access to Essential Services: Many areas lack access to clean water, electricity, healthcare, and other essential services.
- Economic Hardship: Widespread unemployment, inflation, and the destruction of businesses have caused significant economic hardship.
- Mental Health Challenges: The trauma of war, displacement, and loss has led to widespread mental health issues.
- Separation of Families: Millions of families have been separated due to displacement, with many children separated from their parents.
Information Warfare
The conflict in Ukraine has been accompanied by a massive and sophisticated information war, blurring the lines between truth and falsehood and significantly impacting global perceptions of the conflict. Propaganda and disinformation campaigns, employed by both sides and various external actors, aim to manipulate public opinion, influence policy decisions, and undermine the morale of adversaries. The speed and reach of modern communication technologies, particularly social media, have amplified the impact of this information warfare, creating a complex and challenging environment for understanding the true nature of the conflict.
Examples of Misinformation and Propaganda
Numerous examples of misinformation and propaganda have emerged since the start of the conflict. Russian state media, for instance, has consistently portrayed the invasion as a necessary “special military operation” to “denazify” Ukraine, downplaying the scale of civilian casualties and portraying Ukrainian forces as aggressors. Conversely, some Ukrainian sources have exaggerated Russian losses or presented overly optimistic assessments of the battlefield situation. The spread of manipulated or fabricated videos and images, often depicting events out of context or entirely fabricated, has further complicated the information landscape. These tactics aim to shape narratives and influence international perceptions of the conflict, often with the intention of swaying public support or justifying military actions.
The Role of Social Media in Shaping Public Opinion
Social media platforms have become crucial vectors for the dissemination of both accurate and inaccurate information regarding the conflict. The rapid spread of information, often unchecked and unverified, has created an environment where misinformation can quickly gain traction and influence public opinion. Algorithms designed to maximize engagement can inadvertently amplify the reach of misleading content, leading to the formation of echo chambers and reinforcing pre-existing biases. The lack of robust fact-checking mechanisms on many platforms has further exacerbated the problem, allowing false narratives to flourish and shape public understanding of the conflict. Consequently, social media has played a significant role in shaping global perceptions of the conflict, influencing public support for various sides and impacting international policy decisions.
Efforts to Combat Disinformation and Promote Accurate Reporting
Various organizations and governments have implemented initiatives to combat disinformation and promote accurate reporting related to the Ukraine conflict. Fact-checking organizations, such as the Associated Press and Reuters, have dedicated teams to verify information and debunk false claims. Social media platforms themselves have also taken steps, though often criticized as insufficient, to remove or flag misleading content. International organizations, such as the United Nations, have also played a role in disseminating accurate information and counteracting propaganda. However, the scale and sophistication of disinformation campaigns present a significant challenge, requiring a multi-faceted approach involving collaboration between governments, media outlets, tech companies, and civil society organizations.
Disinformation Tactics Employed
| Tactic | Description | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fake News | Completely fabricated stories presented as factual news reports. | A fabricated article claiming Ukrainian forces committed a massacre. | Erodes trust in legitimate news sources, fuels division. |
| Propaganda | Information designed to promote a particular political cause or point of view. | State-sponsored media portraying the invasion as a liberation. | Shapes public opinion, justifies actions. |
| Disinformation | Deliberately false or misleading information. | Manipulated videos showing staged events. | Misleads the public, fuels conflict. |
| Misinformation | Unintentionally false or misleading information. | Unverified social media posts about the conflict. | Creates confusion, hinders understanding. |
Reconstruction and Recovery
The reconstruction of Ukraine after the war presents an immense and multifaceted challenge, requiring a long-term commitment and substantial international cooperation. The scale of destruction, encompassing infrastructure, housing, and critical services, necessitates a comprehensive and strategically planned approach that addresses both immediate needs and long-term sustainable development. The task is not merely about rebuilding what was lost, but about building a more resilient and prosperous future for Ukraine.
The challenges involved are staggering. Beyond the sheer physical destruction, there are significant hurdles related to landmine clearance, the removal of unexploded ordnance, and the remediation of environmental damage caused by the conflict. Furthermore, rebuilding requires addressing issues of governance, corruption, and ensuring equitable distribution of resources. The psychological trauma experienced by the population also necessitates significant investment in mental health services and social support programs.
Economic Recovery Strategies
Ukraine’s economic recovery plan must focus on several key areas. Diversification of the economy away from its reliance on specific sectors affected by the war is crucial. This includes supporting the growth of technology sectors, promoting entrepreneurship, and fostering innovation. Attracting foreign investment will be vital, requiring the creation of a stable and predictable investment climate. Rebuilding critical infrastructure, including transportation networks, energy grids, and communication systems, is paramount to facilitating economic activity and attracting investment. The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) have already pledged significant financial assistance, but continued international support will be essential to ensure the success of these efforts. Examples of successful post-conflict economic recovery include Germany after World War II, which utilized the Marshall Plan for substantial reconstruction, and post-war Japan’s rapid economic growth driven by technological innovation and strategic investments.
Infrastructure Development
Rebuilding Ukraine’s infrastructure will require a phased approach, prioritizing critical needs such as housing, healthcare facilities, and energy supplies. The use of sustainable and resilient building materials and technologies is essential to minimize the environmental impact and ensure the long-term durability of the rebuilt infrastructure. This could include utilizing prefabricated housing units to accelerate construction, employing modern energy-efficient technologies in building designs, and investing in renewable energy sources to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The reconstruction process should incorporate smart city concepts, optimizing resource management and improving the quality of life for citizens. The scale of this task necessitates significant international technical expertise and financial support. Consider the scale of the post-war reconstruction efforts in countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, where international organizations played a key role in rebuilding infrastructure and providing technical assistance.
International Support for Reconstruction
International support is not merely desirable but absolutely essential for Ukraine’s reconstruction. This support must take various forms, including financial aid, technical expertise, and capacity building. International organizations such as the European Union, the United Nations, and the World Bank are already playing a significant role, but greater coordination and commitment are needed. The establishment of a dedicated international reconstruction fund, similar to the Marshall Plan for post-war Europe, would facilitate the efficient allocation of resources and ensure transparency and accountability. Bilateral assistance from individual countries will also be vital, tailored to specific needs and areas of expertise. The level of support should reflect the scale of the destruction and the importance of supporting Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. The success of reconstruction efforts will depend heavily on the sustained and coordinated commitment of the international community.
Post-Conflict Reconciliation Plan
A comprehensive plan for post-conflict reconciliation is crucial for the long-term stability and prosperity of Ukraine. This plan should focus on addressing the root causes of the conflict, promoting inclusive dialogue, and ensuring justice and accountability. Key elements include establishing transitional justice mechanisms, such as truth and reconciliation commissions, to address past grievances and promote healing. Furthermore, measures are needed to ensure the protection of human rights, including the rights of minorities and internally displaced persons. Reintegration programs for veterans and other affected populations are essential to help them transition back into civilian life and contribute to the reconstruction process. Investing in education and civic engagement initiatives will be vital in fostering a shared national identity and promoting social cohesion. Successful reconciliation efforts require a long-term commitment and a focus on building trust and fostering understanding between different groups within society. Similar processes have been attempted in other post-conflict societies, such as South Africa’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which offers valuable lessons in the challenges and complexities of reconciliation.
War Crimes and Accountability
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has witnessed numerous alleged violations of international humanitarian law, raising critical questions about accountability for war crimes. Establishing accountability is a complex process, requiring thorough investigations, credible evidence, and effective prosecution within established legal frameworks. The scale of alleged atrocities necessitates a robust international response to ensure justice for victims and deter future violations.
Alleged War Crimes in Ukraine
The International Criminal Court (ICC) and other international bodies are investigating a wide range of alleged war crimes committed by both sides of the conflict. These include, but are not limited to, indiscriminate attacks on civilian populations, targeting of civilian infrastructure (hospitals, schools, residential areas), the use of prohibited weapons, torture, summary executions, sexual violence, and the forced deportation of Ukrainian civilians to Russia. Specific examples include the bombing of civilian areas like Mariupol, Bucha’s mass graves, and reports of widespread torture and sexual assault in occupied territories. These actions, if proven, constitute serious violations of the Geneva Conventions and other international humanitarian law.
International Efforts to Investigate and Prosecute
The ICC, with its jurisdiction over war crimes, crimes against humanity, and genocide committed on Ukrainian territory since November 2013, has opened an investigation. Other countries, including those within the European Union and the United States, are conducting their own investigations and are supporting the ICC’s efforts. These investigations involve collecting evidence, interviewing witnesses, and analyzing forensic data to build cases against individuals suspected of committing war crimes. The challenge lies in securing cooperation from all relevant parties, particularly in accessing conflict zones and obtaining testimonies from witnesses who may be threatened or intimidated.
Applicable Legal Frameworks
The primary legal framework governing war crimes is international humanitarian law (IHL), comprised of the Geneva Conventions of 1949 and their Additional Protocols. These conventions establish rules for the conduct of armed conflict, protecting civilians and combatants who are hors de combat. The Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC) provides the legal basis for prosecuting individuals responsible for war crimes. National legal systems also play a crucial role, with many states incorporating IHL principles into their domestic laws and having jurisdiction over their own nationals who commit war crimes abroad. The principle of universal jurisdiction allows some states to prosecute individuals for war crimes regardless of where the crimes were committed or the nationality of the perpetrator.
Challenges in Establishing Accountability
Establishing accountability for atrocities in Ukraine faces significant challenges. These include securing access to conflict zones for investigators, gathering sufficient and credible evidence amidst active hostilities, protecting witnesses from intimidation and retaliation, and ensuring fair and impartial trials. Furthermore, the sheer scale of alleged crimes and the involvement of multiple actors complicate the investigative and prosecutorial processes. Political considerations and the lack of cooperation from certain states also hinder efforts to bring perpetrators to justice. The long-term process of collecting evidence, building cases, and conducting trials will require sustained international commitment and resources.
Cultural Heritage
The ongoing war in Ukraine has inflicted devastating damage on the country’s rich cultural heritage, a legacy spanning millennia. The destruction extends beyond physical structures; it represents the erosion of national identity and the loss of irreplaceable historical artifacts. Understanding the extent of this damage and the efforts to mitigate it is crucial for comprehending the full scope of the conflict’s impact.
Damage to Cultural Sites
The conflict has resulted in significant damage to numerous historical sites across Ukraine. Shelling and fighting have directly impacted architectural marvels, museums, and archaeological sites. For instance, the medieval castle in Bakhmut suffered extensive damage from shelling, with parts of its walls and structures crumbling. Similarly, numerous churches, some dating back centuries, have been destroyed or severely damaged, losing irreplaceable religious artifacts and artwork in the process. The destruction extends to less prominent but equally valuable sites – smaller historical buildings, village churches, and local museums holding invaluable collections of regional art and artifacts. These losses represent not only the destruction of physical structures but also the erasure of local histories and cultural identities.
Preservation and Protection Efforts
Despite the ongoing conflict, significant efforts are underway to preserve and protect Ukraine’s cultural heritage. Ukrainian authorities, along with international organizations like UNESCO, are working to document damage, secure vulnerable sites, and implement emergency preservation measures. This includes the evacuation of artifacts from conflict zones to safer locations, both within Ukraine and abroad. Furthermore, digital documentation projects are underway to create virtual records of damaged or destroyed sites, ensuring their memory is preserved even if the physical structures are lost. International collaborations are crucial, providing financial and technical support to aid in preservation efforts. These efforts, though hampered by the ongoing war, represent a crucial commitment to safeguarding Ukraine’s cultural identity for future generations.
Significant Cultural Sites Affected
The following list highlights some significant cultural sites impacted by the conflict, illustrating the breadth and depth of the damage. This list is not exhaustive, as the situation is constantly evolving and new damages are being reported regularly.
- Saint Sophia’s Cathedral in Kyiv: While not directly hit, this UNESCO World Heritage site faced threats and required increased security measures during the initial stages of the invasion.
- Churches and Monasteries in Eastern Ukraine: Numerous historical religious structures in regions like Luhansk and Donetsk have suffered significant damage or destruction from shelling and fighting.
- National Museum of the History of Ukraine in the Second World War in Kyiv: This museum, though not directly hit, required enhanced security measures and faced the risk of potential damage.
- Archaeological Sites: Numerous ancient settlements and burial grounds have been damaged or destroyed, resulting in the loss of irreplaceable historical and archaeological data.
- Local Museums and Archives: Smaller museums and archives across the country have suffered losses due to looting, damage from fighting, or the inability to maintain proper preservation conditions.
Long-Term Consequences
The war in Ukraine has unleashed a cascade of events with far-reaching and potentially irreversible consequences, extending beyond the immediate battlefield. The long-term impacts will reshape the geopolitical landscape of Europe and beyond, influencing international relations, regional security, and the very fabric of Ukrainian society for decades to come. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Geopolitical Restructuring and Regional Instability
Shifts in the European Security Architecture
The war has fundamentally altered the European security architecture. NATO’s expansion eastward, previously a point of contention, has now become a solidified reality, driven by the perceived threat from Russia. This expansion, while bolstering the security of Eastern European nations, also risks further escalating tensions with Russia and potentially creating new fault lines. The increased military presence in the region, coupled with the ongoing conflict, will likely lead to a prolonged period of heightened military preparedness and an arms race, impacting national budgets and potentially diverting resources from other crucial sectors like healthcare and education. For example, Finland and Sweden’s recent accession to NATO demonstrates a significant shift in the geopolitical balance, reflecting a direct response to Russia’s aggression.
Increased Regional Tensions and Potential for Future Conflicts
The war in Ukraine has created a volatile security environment, increasing the risk of spillover conflicts in neighboring regions. The potential for renewed conflicts in the Transnistria region of Moldova, or further instability in the Caucasus, is a tangible concern. Russia’s actions have emboldened other authoritarian regimes, potentially inspiring similar actions elsewhere. This increased instability could lead to a rise in regional proxy wars, fueled by external actors vying for influence and control. The unresolved territorial disputes in the region, such as the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, could be reignited, creating further instability and humanitarian crises. This illustrates the potential for a domino effect, where the Ukrainian conflict acts as a catalyst for broader regional instability.
A Hypothetical Future for Ukraine
One possible scenario envisions a post-war Ukraine significantly altered but ultimately resilient. After a negotiated settlement, perhaps involving territorial concessions, Ukraine might undergo a period of extensive reconstruction supported by international aid. The country could emerge as a stronger, more unified nation, deeply integrated with the European Union and NATO. However, this scenario also assumes a sustained commitment from Western allies and a successful effort to address deep-seated corruption and rebuild shattered infrastructure. Alternatively, a prolonged conflict could lead to a fragmented Ukraine, with lasting political instability and economic hardship. This scenario would depend on several factors, including the level of continued Russian aggression, the effectiveness of international sanctions, and the resilience of the Ukrainian government and people. This hypothetical future highlights the inherent uncertainty and the wide range of possible outcomes.
End of Discussion
The situation in Ukraine presents a complex and evolving narrative with profound implications for global security and stability. While the immediate focus remains on the ongoing conflict and humanitarian crisis, the long-term consequences, including the need for reconstruction, accountability for war crimes, and the potential for future conflicts, demand careful consideration. Understanding the multifaceted nature of this crisis – from the military strategies employed to the socio-economic impacts and international responses – is crucial for navigating the challenges ahead and fostering a path toward lasting peace and recovery.






